PE foam insulation has a closed-cell structure. This helps block heat and sound. It works in very hot and cold temperatures. It can handle from -292°F to 302°F. The closed cells keep air inside. This stops heat from escaping and lowers noise. Many industries use pe foam insulation. It is light and does not soak up water. The table below shows how pe foam works in buildings:
Material | Thermal Conductivity (λ) W/(m·K) |
PE foam | 0.036 – 0.041 |
People pick pe foam because it works well and is dependable.
Key Takeaways
PE foam insulation stops heat, sound, and water from passing through. Its closed-cell structure helps keep rooms comfy and quiet.
It is light, bends easily, and lasts a long time. This makes it simple to put in buildings, cars, and packages.
PE foam works well in very hot or cold places. It does not let water, chemicals, or hits damage it. This means it lasts a long time.
A shiny aluminized layer helps bounce heat away. This saves energy in sunny or hot places.
PE foam has many good points, but it can burn fast. So, you should check fire safety rules before using it.
PE Foam Insulation

What Is PE Foam
Polyethylene foam, or pe foam, is light and bends easily. It is made by mixing polyethylene resin with blowing agents. This makes many tiny closed cells filled with air. These cells give pe foam insulation special features. It keeps out water, softens impacts, and stops heat and sound. Many industries use it because it stays strong in tough places.
Polyethylene foam has closed cells. Each cell is shut tight. Water and air do not move through it easily.
It stands up to chemicals like oils, acids, and solvents. It also takes in shocks and vibrations.
Its density goes from 0.01 to 0.14 g/cm³. Higher density means it is stronger but less bendy.
Makers can add flame retardants to help it resist fire. They check fire safety with UL 94 tests. Some types put out flames by themselves, but others burn faster.
Extruded polyethylene foam is used in packaging, building, and cars.
Note: Polyethylene foam is great at keeping out water, floating, and softening bumps. These things make it a top pick for many uses.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam
Cross-linked polyethylene foam, called XLPE foam, works even better. Makers join the polymer chains with heat or chemicals. This makes the structure tighter and more stable. It helps the foam bend, last longer, and resist chemicals and weather.
Property | Performance Range / Value |
Density (kg/m³) | 20±5 to 200±30 |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.040 to 0.075 |
Temperature Resistance | -40°C to +120°C |
Water Absorption (%) | ≤ 8% |
Tensile Strength (MPa) | ≥ 0.12 to ≥ 1.2 |
Elongation (%) | ≥ 80% to ≥ 130% |
Compressed Distortion (%) | ≤ 7% to ≤ 11% |
Cross-linked polyethylene foam has many good points:
Small, even closed cells help keep heat in or out.
It stands up to weather, chemicals, and sunlight.
It stays bendy and soft, even in hard places.
It is still light, so it is easy to put in.
Many industries pick cross-linked polyethylene foam for steady results. It works in hot and cold places. It also passes tough safety and strength rules. Newer types have flame retardants for better fire safety. These changes help in building, car, and airplane jobs.
Tip: Cross-linked polyethylene foam often lasts longer and bends better than other insulation. It keeps its shape and features, even when pressed or stretched.
Some pe foam insulation has a shiny aluminized layer. This shiny part reflects heat away. It gives extra thermal protection, especially in buildings and HVAC systems.
Studies show pe foam insulation works as well as other materials. It gives good thermal results, saves money, and lasts a long time. But fire safety and how long it lasts are still important when picking insulation.
Features
Closed-Cell Structure
Polyethylene foam has a closed-cell structure. Each cell holds air inside. This stops heat and sound from passing through. The foam is light but also strong. Water and air cannot move through it easily. Most sheets have densities between 20 and 200 kg/m³. Their thickness ranges from 1 mm to 100 mm. Laminated sheets can be as thick as 200 mm. The table below shows the usual density and thickness for these foam sheets:
Property | Typical Range / Values |
Density (kg/m³) | 20 to 200 |
Thickness (mm) | 1 to 100 (block), up to 200 |
This structure helps the foam keep its shape. It also makes the foam tough and hard to break. Many builders use this foam because it lasts long and does not soak up much water.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene foam does not let water in. Its closed cells stop water from getting inside, even when it is wet. Studies show that this foam keeps out water, even in hot and damp places. Polyethylene foam also stands up to many chemicals, like oils and acids. Some types are even better at resisting chemicals and are safer to use. This makes the foam a good pick for places with water or chemicals.
Note: Polyethylene foam works well in hard places, like cold storage or chemical plants.
Sound and Vibration Absorption
Polyethylene foam can soak up sound and vibration. Its closed cells help block noise. Thicker foam sheets block more sound, especially at some sound levels. A 1-inch thick piece works best for blocking sound from 100 to 6400 Hz. The foam also handles shaking and bumps well. Tests show that how thick and dense the foam is, and the temperature, change how much energy it can take in. This makes it good for lowering noise and stopping damage in buildings, cars, and packages.
Polyethylene foam helps make walls and floors quieter.
It keeps things safe from bumps during shipping.
It helps machines run quietly by soaking up shaking.
Tip: For better sound and bump protection, use thicker or denser polyethylene foam sheets.
How It Works
Thermal Insulation
PE foam insulation has a closed-cell structure. Air gets trapped inside each cell. This stops heat from moving through the foam. The air acts like a wall. It slows down heat going from one side to the other. That is why PE foam is good for thermal insulation in buildings, pipes, and HVAC systems.
Scientists tested foams like PE foam. They found these foams can have very low thermal conductivity, as low as 32.4 mW·m−1·K−1. This means heat does not move through the foam easily. The foam helps keep rooms warm in winter. It also keeps rooms cool in summer. This can help lower energy bills because less heat escapes or comes in.
Builders use PE foam insulation because it works in many temperatures. It stays strong in both cold and hot places. The foam does not lose its shape or break down. Some PE foam has a shiny aluminized layer. This shiny part reflects heat away. It gives extra thermal insulation, especially for roofs and walls in the sun.
Tip: Aluminized PE foam insulation is best for places with lots of sunlight or radiant heat. The shiny layer bounces heat back and keeps spaces cooler.
PE foam insulation comes in many thicknesses and densities. Thicker foam gives better thermal insulation. Builders can pick the right type for each job.
Acoustic Insulation
PE foam insulation also helps block sound. Its closed-cell structure stops sound waves from getting through. The foam soaks up noise and cuts down on echoes in rooms. This makes it helpful in homes, offices, and factories.
In factories, engineers use foams with PE foil lamination to control noise.
The PE foil lamination keeps the foam safe from water and chemicals but still blocks sound.
In building, foam insulation like PET and EPS foams also block sound well. The table below lists some results:
Material Type | Thickness | Frequency (Hz) | Sound Transmission Loss (dB) | Weighted Sound Reduction Index Increase (dB) |
PET Foam | 15 cm | 1600+ | ~10 | N/A |
Foamed Plastics (general) | N/A | N/A | N/A | +3.5 (compared to reference) |
These numbers show that foam insulation can make rooms quieter by blocking noise.
PE foam insulation gives both thermal and acoustic insulation in one product. It keeps spaces comfy and quiet. Builders and engineers use it in homes, offices, and factories because it works well and lasts long.
Applications
Building and Construction
Builders use pe foam insulation in many building areas. It works in roofs, walls, floors, air ducts, and pipes. The closed-cell structure keeps heat inside in winter. It also keeps heat out in summer. This foam blocks moisture and sound too. Building codes, like the 2021 International Building Code (IBC), have rules for foam plastic insulation. These rules help with fire safety, weather, and moisture. The IBC and other standards, such as NFPA 285 and ICC 1100-2019, keep buildings safe when using foam insulation. Builders often pick foam plastic sheathing for foundation walls. This helps stop heat loss and condensation. ASCE 32-01 gives advice for using foam insulation in shallow foundations that need frost protection.
Common uses in construction:
Note: PE foam insulation works well in homes, small businesses, and light factories.
Packaging
PE foam is important for packaging. It protects things from damage during shipping. It also keeps items fresh by giving insulation. Reports show that PE foam cushions and soaks up shocks. This helps protect fragile and expensive items. Its thermal resistance and moisture barrier keep products safe from heat and water. Many companies want packaging that is light, strong, and good for the environment. More online shopping has made this packaging even more popular.
Key benefits in packaging:
Automotive and Industrial
Car makers and factories use PE foam for many jobs. It is light, strong, and bends easily. In cars, it helps lower weight and saves fuel. It also insulates, absorbs shocks, and blocks noise. PE foam is found in car seats, interiors, gaskets, and soundproofing. Electric cars use it for battery insulation and safety. In factories, it gives thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and stops vibration. Makers use special ways to shape PE foam for each job. They add materials to make it safer from fire and better at absorbing impacts.
Main uses in automotive and industry:
Interior and seat padding
Gaskets and soundproofing
Battery insulation in electric vehicles
Vibration dampening in machinery
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Preventing Heat Loss
PE foam insulation helps keep heat inside in winter. It also blocks heat from coming in during summer. The closed-cell structure traps air inside the foam. This slows down how fast heat moves through it. Rooms stay warm or cool for a longer time. Builders use this insulation to help homes and offices save energy. When they put in PE foam, less heat gets out through walls, roofs, and floors.
Numerical studies show how insulation changes heat loss. The table below compares the thermal properties of different foam insulations:
Insulation Material | Thermal Conductivity λ (W/m·K) | Heat Transfer Coefficient Uc (W/m²·K) | Linear Heat Transmittance Coefficient Ψ (W/m·K) |
XPS (extruded polystyrene) | 0.034 (declared) | 0.230 | 0.00823 |
XPS (measured) | 0.035 | 0.234 | 0.00866 |
EPS (expanded polystyrene) | 0.032 (declared) | 0.222 | 0.00788 |
EPS (measured) | 0.033 | 0.226 | 0.00814 |
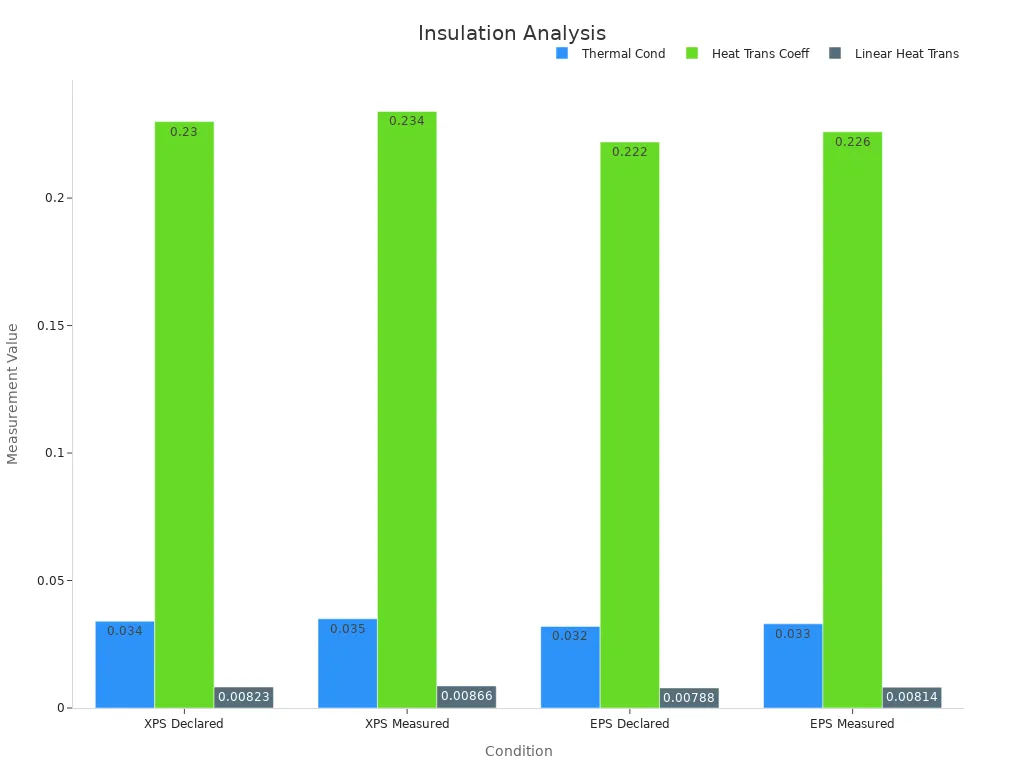
These numbers show that insulation works differently in real life. Even small changes in thermal conductivity can change heat loss. New computer models help predict heat loss faster and better. This helps builders pick the best insulation for saving energy.
Cost Savings
Insulation that stops heat loss helps lower energy bills. When a building keeps heat in, heaters and air conditioners do not run as much. This means people spend less money each month. Over time, these savings can be big. Most PE foam insulation lasts for many years. It does not need much care or fixing. Many people see that the cost of insulation pays off with lower bills.
PE foam insulation stays strong and works well for years.
It does not break down easily because it resists water and chemicals.
Most people only need to check it sometimes.
Tip: Picking the right insulation can help save energy and money for a long time.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
PE foam insulation gives many good things for builders and makers. It is very light, so people can move and put it in place easily. Workers can cut and shape it with simple tools. The foam bends and fits into small spaces or wraps around pipes. Many people pick PE foam because it does not let water or chemicals in. This helps it last longer in tough places.
Lightweight: Simple to move and put in.
Flexible: Fits many shapes and places.
Durable: Keeps out water, chemicals, and damage.
Cost-effective: Saves money on materials and work.
Shock Absorption: Protects things during shipping and use.
Recyclable: Easier to recycle than some other foams.
A new report says cross-linked PE foam is stronger and lasts longer. This makes it a top pick for cars and buildings. Low-density PE foam is used a lot in packaging because it is cheap and soft. High-density types are stronger, so they help in building and support jobs. The world market for PE foam keeps growing because it works well and costs less.
Tip: PE foam insulation gives thermal insulation, keeps out water, and softens bumps all in one.
Disadvantages
PE foam insulation also has some problems. It can catch fire fast and spread flames quickly. Tests show PE foam burns fast and makes lots of heat and smoke. This makes it risky for fires, especially in tall buildings. Some places do not allow it in public areas for this reason. Special coatings can help stop fires, but these cost more and may not fix every problem.
Flammable: Burns fast and spreads fire.
Toxic Gases: Makes harmful gases when burning.
Lower Strength: Not as strong as EPS or XPS foams.
Possible Cracking: Can crack or break over time.
Not Biodegradable: Still adds to trash, but recycles better than EPS.
Feature | PE Foam | EPS Foam | XPS Foam |
R-Value | Moderate | High | Higher |
Density | Low/Medium | Low | Medium |
Compressive Strength | Moderate | High | Higher |
Moisture Resistance | High | High | Very High |
Flammability | High | High | High |
Recyclability | Good | Poor | Poor |
Studies show natural fiber insulations like sheep wool and hemp are safer and better for the earth. EPS and XPS foams are stronger and keep heat in better, but they hurt the environment more. PE foam gives a good mix of price, how it works, and recycling, but people must think about fire risks and lower strength.
Note: Always check local building rules before using PE foam insulation, especially for fire safety.
PE foam insulation works well for many projects. It keeps heat in, blocks noise, and resists water. Many builders choose it because it is light and easy to use. Studies show closed-cell spray foam gives high R-values, stops drafts, and helps the environment when installed by experts using low GWP products. Some limits include fire risk and lower strength. People should check their needs and compare PE foam to other types before choosing.
FAQ
What is the main use of PE foam insulation?
PE foam insulation helps keep buildings warm or cool. It blocks heat, sound, and moisture. Builders use it in walls, roofs, and floors. Many people also use it for packaging and car parts.
Is PE foam insulation safe for homes?
PE foam insulation is safe when installed correctly. It does not release harmful chemicals during normal use. People should check local fire codes before using it in large amounts.
How long does PE foam insulation last?
PE foam insulation can last for many years. It resists water, chemicals, and damage. Most people do not need to replace it often.
Can PE foam insulation be recycled?
Yes, many recycling centers accept PE foam insulation. It is easier to recycle than some other foams. People should check local recycling rules.
Does PE foam insulation stop noise?
PE foam insulation absorbs sound and reduces noise. It works well in walls and floors. Many builders use it to make rooms quieter.








